| Solution 1 |
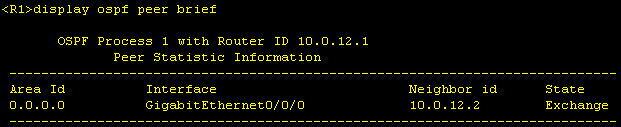
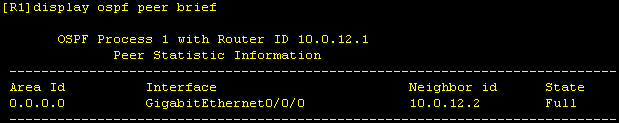
We see that on R1, OSPF peering remains in state "Exchange" and does not go to "Full".
There can be various reasons for this, including an MTU mismatch. If the
As we can see, the MTU is configured differently on the interfaces. We therefore change the MTU on R1 to the standard value of 1500 bytes.
After that, OSPF peering between R1 and R2 comes up and is in "Full" state.
|
| Solution 2 |
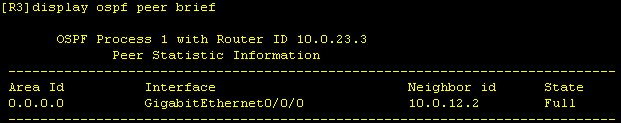
We do not have OSPF peering between R2 and R3. First, we check the R2 interface G0/0/1 configuration. Here we see that an inbound ACL is configured.
We see that the ACL only has one rule, which discards everything.
Since we are not allowed to delete or remove any ACLs from the interface according to the General Rules of the Troubleshooting Lab, we must add a permit entry before the deny entry.
Since OSPF peering still does not come up after this adjustment, let's take a look at the configuration on R3. |
| Solution 3 |
On R3, we also first check the configuration on interface G0/0/0. [R3]display current-configuration interface g0/0/0#interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0ip address 10.0.23.3 255.255.254.0 #
What we see here is that the subnet mask is incorrect according to the layout (/23 instead of /24). For the OSPF peering, the subnet mask must be the same on both side, which is why we correct it on R3.
After that, OSPF peering to R2 comes up and is in “Full” state.
|
| Solution 4 |
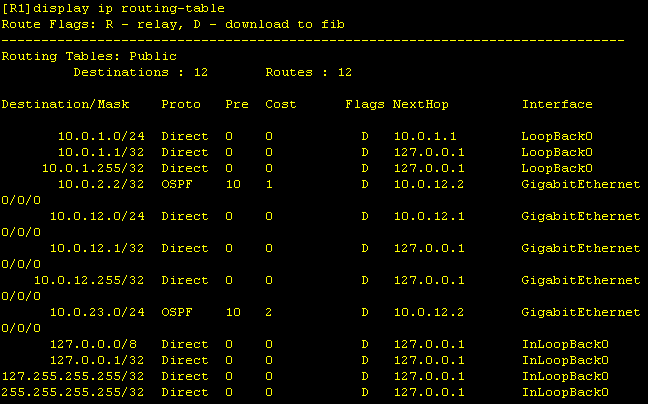
Now all OSPF peerings are in place. However, if we check the routing table on R1, we still see that the Loopback0 network from R3 is missing and therefore the ping is not working.
On R3, we can see with [R3]display c c ospf#ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.0.3.0 0.0.0.0 network 10.0.23.0 0.0.0.255 #
Here we see that the network statement for the Loopback0 network does not match. We can correct this in two ways. 1) We change the network and leave the wildcard mask the same
2) We leave the network and change the wildcard mask
Both variants lead to the same result, in that the Loopback0 network of R3 is now propagated. |
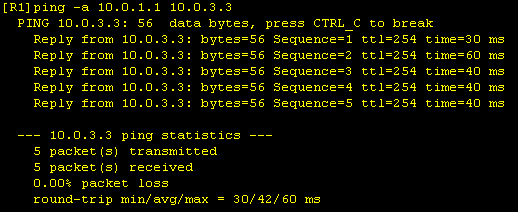
| Solution 5 |
Now we can ping from the R1 Loopback0 network to the Loopback0 network of R3, which is required as a final test.
|
| Notes |
|
Solutions File
Download and start the Solutions Topo file below to check the final configuration.
Download Huawei HCIA Datacom Demo Troubleshooting Lab eNSP Topo File Solutions